canine cruciate tear test|canine cruciate ligament rupture : company Diagnosing complete tears of the CrCL is easily accomplished by a veterinarian using a combination of gait observations, physical examination findings, and radiography (X-rays). By contrast, partial CrCL tears may be more challenging to diagnose and may require visual inspection via arthrotomy, mini-arthrotomy, or arthroscopy to confirm.
The global steam autoclaves market size was valued at USD 3.2 billion in 2024 and is expected to exhibit growth at a CAGR of 8.3% from 2025 to 2034, driven by rise in prevalence of nosocomial infections.
{plog:ftitle_list}
$79.99
aflatoxin b1 quantification in aqueous samples using elisa kit
cruciate ligament rupture treatment for dogs
Diagnosing complete tears of the CrCL is easily accomplished by a veterinarian using a combination of gait observations, physical examination findings, and radiography (X-rays). By contrast, partial CrCL tears may be more challenging .In dogs, the most common knee injury is a rupture or tear of the cranial cruciate ligament. Humans have a similar anatomical structure to the dog's knee, but the ligaments are called the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) tears are one of the most prevalent orthopedic issues affecting dogs, akin to the ACL injury in humans. This ligament is crucial for stabilizing the knee (or stifle) joint, especially during movement. When a CCL tear occurs, it leads to pain, instability, and difficulty walking, most often resulting in lameness .
cranial cruciate ligament rupture dog
Specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the CCL are the “cranial drawer test” and the “tibial thrust test.” These tests confirm abnormal motion in the knee and hence a rupture of the CCL.
Value of low-field magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing meniscal tears in the canine stifle: a prospective study evaluating sensitivity and specificity in naturally occurring cranial cruciate ligament deficiency with arthroscopy as the gold standard.Diagnosing complete tears of the CrCL is easily accomplished by a veterinarian using a combination of gait observations, physical examination findings, and radiography (X-rays). By contrast, partial CrCL tears may be more challenging to diagnose and may require visual inspection via arthrotomy, mini-arthrotomy, or arthroscopy to confirm.
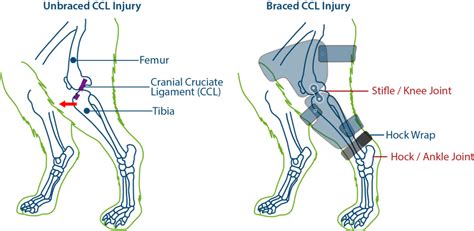
The CCL in dogs is analogous to the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) in people. This ligament connects the femur, the bone in the thigh, to the tibia, or shin bone, in the dog’s hind leg. It is located in the “knee” joint (called the stifle in .The cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) is a key stabilizing ligament in the knee (or stifle) joint in dogs. It works similarly to the ACL in humans. It works similarly to the ACL in humans. However, unlike humans, CCL injuries in dogs are more often caused by gradual degeneration over time rather than a sudden traumatic event.
Canine Cranial Cruciate Ligament Diagram. Finding the Rupture. The ruptured cruciate ligament is the most common knee injury of dogs; in fact, chances are that any dog with sudden rear leg lameness has a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament rather than something else. Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease (CCLD) is a condition involving the tearing or degeneration of one of the ligaments within your pet's knee joint, known as the cranial cruciate ligament (CCL). 4 min read. If your dog goes lame in one of their hind legs, they may have torn or ruptured their cranial cruciate ligament, or CCL -- similar to the ACL in humans. This ligament connects the.In dogs, the most common knee injury is a rupture or tear of the cranial cruciate ligament. Humans have a similar anatomical structure to the dog's knee, but the ligaments are called the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments.
Cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) tears are one of the most prevalent orthopedic issues affecting dogs, akin to the ACL injury in humans. This ligament is crucial for stabilizing the knee (or stifle) joint, especially during movement. When a CCL tear occurs, it leads to pain, instability, and difficulty walking, most often resulting in lameness .Specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the CCL are the “cranial drawer test” and the “tibial thrust test.” These tests confirm abnormal motion in the knee and hence a rupture of the CCL.Value of low-field magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing meniscal tears in the canine stifle: a prospective study evaluating sensitivity and specificity in naturally occurring cranial cruciate ligament deficiency with arthroscopy as the gold standard.Diagnosing complete tears of the CrCL is easily accomplished by a veterinarian using a combination of gait observations, physical examination findings, and radiography (X-rays). By contrast, partial CrCL tears may be more challenging to diagnose and may require visual inspection via arthrotomy, mini-arthrotomy, or arthroscopy to confirm.
The CCL in dogs is analogous to the ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) in people. This ligament connects the femur, the bone in the thigh, to the tibia, or shin bone, in the dog’s hind leg. It is located in the “knee” joint (called the stifle in .The cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) is a key stabilizing ligament in the knee (or stifle) joint in dogs. It works similarly to the ACL in humans. It works similarly to the ACL in humans. However, unlike humans, CCL injuries in dogs are more often caused by gradual degeneration over time rather than a sudden traumatic event. Canine Cranial Cruciate Ligament Diagram. Finding the Rupture. The ruptured cruciate ligament is the most common knee injury of dogs; in fact, chances are that any dog with sudden rear leg lameness has a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament rather than something else. Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease (CCLD) is a condition involving the tearing or degeneration of one of the ligaments within your pet's knee joint, known as the cranial cruciate ligament (CCL).
cranial cruciate ligament rupture diagnostic test
canine cruciate ligament rupture
aflatoxin b1 quantification in aquous samples using elisa kit
aflatoxin b1 quantification using elisa kit
M3 UltraFast ® Sterilizer (Refer to the ‘Maintenance’ section of the User’s Guide for further details of scheduled care). da I LY 1. Clean External Surfaces / t ray & Chamber A. Wash unit .
canine cruciate tear test|canine cruciate ligament rupture